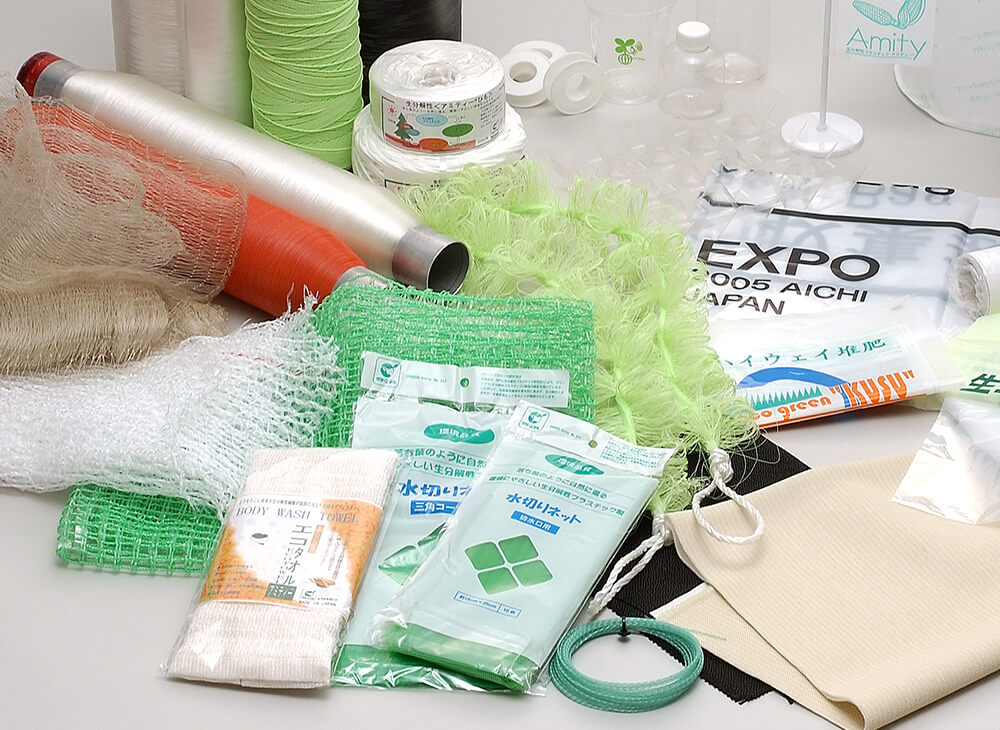
Ordinary plastics, which are made from fossil fuels, have become indispensable in our lives. However, because they emit CO2 when burned and are difficult to decompose, they have an impact on marine plastic pollution and other global environmental issues.
In this context, biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics are attracting attention as "environmentally friendly plastics."
In this article, we will explain what biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics are, the differences between them, and their respective characteristics.
table of contents
・Biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics
-What are biodegradable plastics?
-What is biomass plastic?
・Difference between biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics
・Features and types
・Characteristics of biodegradable plastics
・Types of biodegradable plastics
・Characteristics of biomass plastics
・Types of biomass plastics
・Disadvantages
・About the mark
・About the "Amity™" bioplastic product series
・Introduction of biodegradable plastic products
·Stretch film
・Compost bag
・Sandbags
Yarn
・Introduction of biomass plastic products
・Draining net
·Shopping bag
Biodegradable and biomass plastics
-What are biodegradable plastics?
Biodegradable plastics are exactly what they sound like: plastics that have the property of being decomposed by the action of living organisms, and the name focuses on this function. The main raw materials are plants such as corn, but the "raw materials" are not mentioned. Although they can be used in the same way as regular plastics, after use they are decomposed to the molecular level by the action of microorganisms present in nature, and ultimately circulate back into nature as water and carbon dioxide. This environmentally friendly plastic material is called "biodegradable plastics."
-What is biomass plastic?
The word biomass means "renewable, organic resources derived from living organisms, excluding fossil resources." In other words, it is a plastic made from plants, and since the name focuses on the raw materials, it does not mention whether it "decomposes" or not. Although it can be used in the same way as regular plastics, since it is made from plants, no carbon dioxide is generated during production, and even if carbon dioxide is generated during combustion at the time of disposal, it does not actually increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, making it an environmentally friendly plastic material.
This logic is called carbon neutral.
The difference between biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics
As such, the main raw materials for both biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics are plants such as corn, sweet potatoes, potatoes, and sugar cane.
From the perspective of after use, biodegradable plastics are "environmentally friendly plastics that return to nature," while biomass plastics are "environmentally friendly plastics during the manufacturing process" from the perspective of raw materials.
Biodegradable plastics are derived from plants and decompose naturally, making them a more environmentally friendly plastic material that is closer to a natural circulation system.
However, due to its tendency to decompose, its period of use is limited, which also limits the applications for which it can be used.
Biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics are collectively called "bioplastics."
Characteristics and types
・Characteristics of biodegradable plastics
Degradability
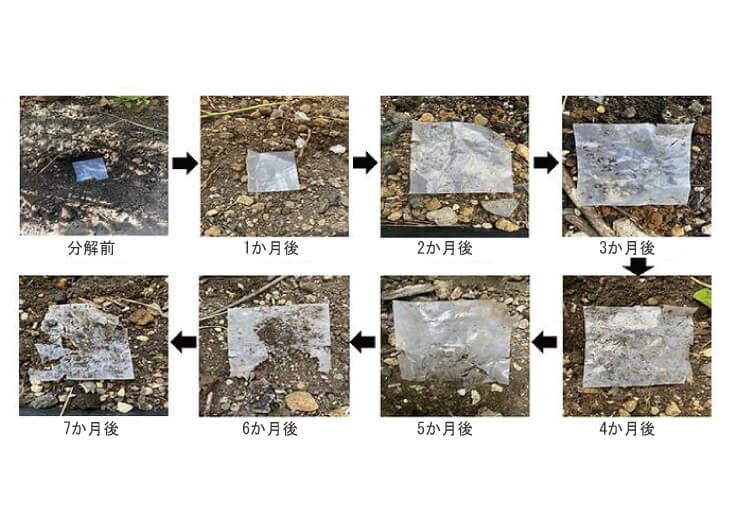
Biodegradable plastics have the property of being completely decomposed by the action of living organisms. Ordinary plastics are said to be oxidatively decomposable, and when exposed to light or heat, the additives cause the plastic to break down and break apart. This phenomenon is called microplastics.
[Disassembly photos]
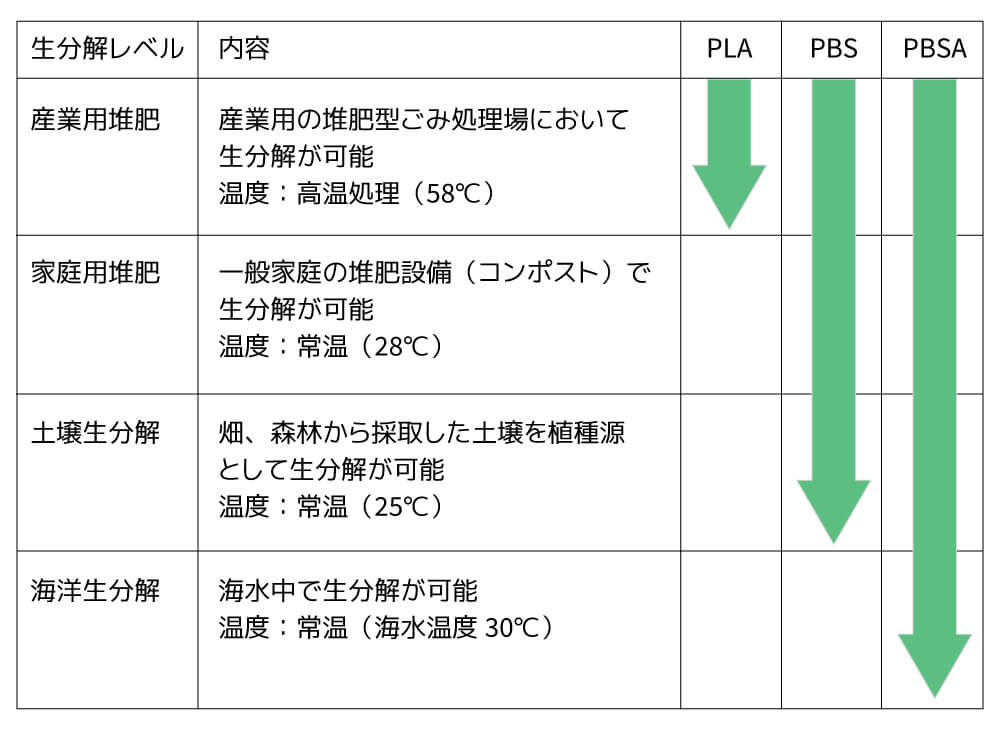
[Decomposition level]
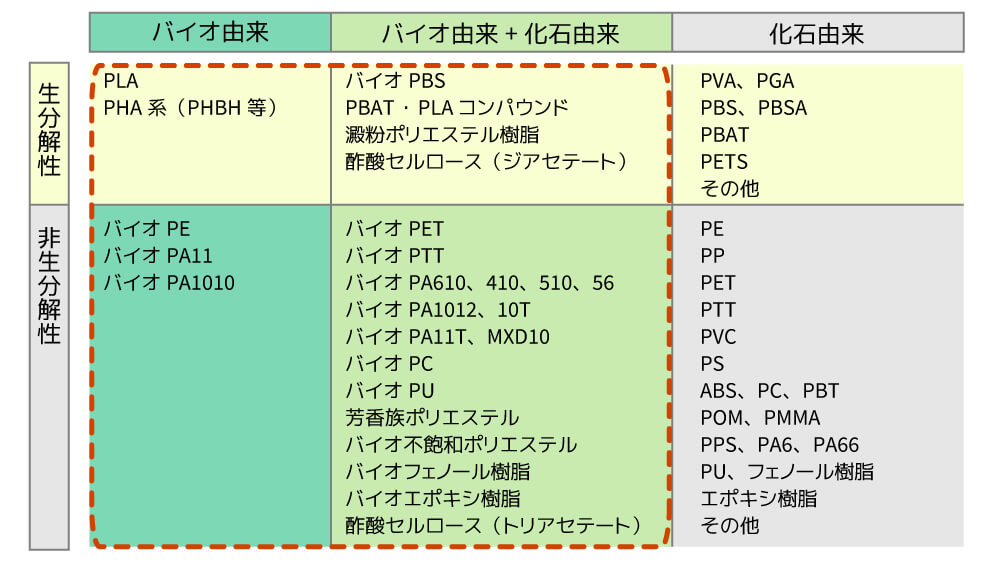
・Types of biodegradable plastics
Biodegradable plastics can be broadly divided into three categories.
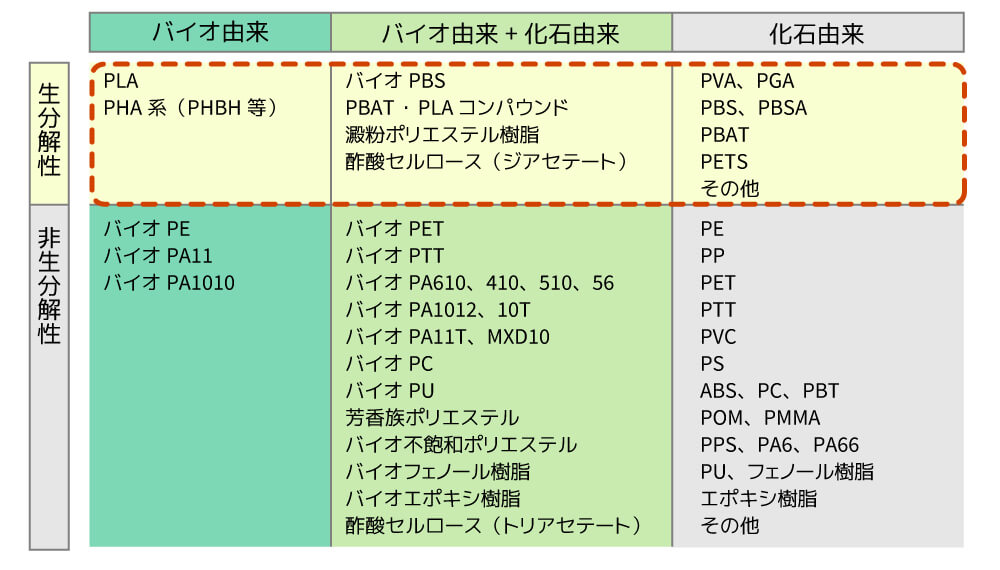
1: Bio-derived
This refers to a material that utilizes the characteristic of microorganisms to accumulate polyester in their bodies, such as polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), an energy substance found in microorganisms, and a type of material called polylactic acid (PLA) made by polymerizing sugars from plants such as corn and sugar cane.
2. Fossil origin
This mainly refers to biodegradable polyester raw materials that break down into harmless, non-toxic compounds, such as the water-soluble polymer polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyglycolic acid (PGA), which is used as medical sutures.
3. A mix of bio-based and fossil-based materials
These materials, such as cellulose acetate made from cellulose (polysaccharides) such as wood or cotton, and BioPBS™ made from plant-derived succinic acid, are bio-based materials that have improved upon the drawbacks of bio-based materials, such as heat resistance, compatibility, and flexibility, while still being able to ultimately decompose into water and carbon dioxide.
PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol, PGA: Polyglycolic acid, PBS: Polybutylene succinate, PBSA: Polybutylene succinate-co-adipate, PBAT: Polybutylene adipate terephthalate, PETS: Polyethylene terephthalate succinate, PE: Polyethylene, PP: Polypropylene, PET: Polyethylene terephthalate, PTT: Polytrimethylene terephthalate, PVC: Polyvinyl chloride, PS: Polystyrene, ABS: Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin, PC: Polycarbonate, PBT: Polybutylene terephthalate, POM: Polyacetal, PMMA: Polymethyl methacrylate, PPS: Polyphenylene sulfide, PA: Polyamide, PU: Polyurethane, PLA: Polylactic acid, PHA: Polyhydroxyalkanoate, PHBH: 3-hydroxybutyric acid-3-hydroxyhexanoic acid copolymer polyester
・Characteristics of biomass plastics
◎A wide variety of processed products
There are a wider variety of biomass plastics available from different raw materials compared to biodegradable plastics.
Therefore, plastic bags, packaging containers, packaging film inks, textile products, electrical and information equipment, Office Automation There is a wide range of processed products, including equipment.
・Types of biomass plastics
Biomass plastics can be broadly divided into two categories.
1: Bio-derived
The most typical bio-PE (bio-polyethylene) is produced by fermenting sugarcane to produce sugar and bioethanol, which is then refined and polymerized to produce polyethylene. Because oxygen is generated during the growth of sugarcane, it is said that carbon dioxide emissions during the manufacturing process can be reduced by up to 70 % compared to petroleum-derived polyethylene (PE).
2: A mix of bio-based and fossil-based materials
The most representative bio-PET, as the name suggests, is made from plant-derived rather than petroleum-derived "polyethylene terephthalate resin," the raw material used in PET bottles, etc. Petroleum-derived "polyethylene terephthalate resin" is made from terephthalic acid (polymerization ratio 70 %) and monoethylene glycol (polymerization ratio 30 %), but this product replaces the 30 % of "monoethylene glycol" with sugarcane pomace (blackstrap molasses).
*In recent years, bio-PET that is 100% plant-based has also been developed.
PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol, PGA: Polyglycolic acid, PBS: Polybutylene succinate, PBSA: Polybutylene succinate-co-adipate, PBAT: Polybutylene adipate terephthalate, PETS: Polyethylene terephthalate succinate, PE: Polyethylene, PP: Polypropylene, PET: Polyethylene terephthalate, PTT: Polytrimethylene terephthalate, PVC: Polyvinyl chloride, PS: Polystyrene, ABS: Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin, PC: Polycarbonate, PBT: Polybutylene terephthalate, POM: Polyacetal, PMMA: Polymethyl methacrylate, PPS: Polyphenylene sulfide, PA: Polyamide, PU: Polyurethane, PLA: Polylactic acid, PHA: Polyhydroxyalkanoate, PHBH: 3-hydroxybutyric acid-3-hydroxyhexanoic acid copolymer polyester
Disadvantages
While biodegradable plastics and biomass plastics have the advantage of being environmentally friendly, they have the disadvantage of being more expensive than regular plastics and requiring higher manufacturing costs when commercializing them.
Furthermore, Japan has a low agricultural self-sufficiency rate, and is forced to import the raw materials, corn and sugarcane. The inability to procure them domestically and the unstable cost price are also reasons why bioplastics have not been widely adopted.
Another reason is that while in Europe and the United States, waste is generally disposed of in soil, in Japan, it is more common to dispose of it in combustible form, which means there is less awareness of the need for waste decomposition.
About the mark
In Japan, there are marks designated by the Japan Bioplastics Association and the Japan Organics Resources Association. We manufacture products that have passed the inspections of both associations.
For details on the marks, please visit the official website of each association.
 |
 |
 |
| Biodegradable plastic mark | Biodegradable biomass plastic mark | Biomass Mark |
About the "Amity ™" bioplastic product series
We have been manufacturing and developing bioplastics since 1985, and our brand name "Amity ™" has earned us a high reputation in Japan.
Introduction of biodegradable plastic products
· Stretch film
This stretch film is made from 100% biodegradable plastic, which is environmentally friendly. Its performance and ease of use as a stretch film are the same as regular polyethylene films. After use, it can be disposed of in the same way as regular polyethylene films.
Product page: https://www2.chukoh.co.jp/products/eco-products/stretch_film/
・Compost bags (garbage bags)
Food waste bags are used by local governments all over the country. In particular, in agricultural regions, they are useful for making high-quality compost. They were also used as garbage bags at the 2005 "EXPO 2005 Aichi" site.
・Sandbags
Since it decomposes in soil, there is no need to collect it or dispose of it as industrial waste, which contributes to reducing disposal costs.
Yarn
This is the thread that is the basis for woven products such as sandbags. We can provide not only products but also just the thread.
Introduction of biomass plastic products
・Draining net
The antibacterial effect of polylactic acid prevents slime from building up in the sink. The soft, stretchy thread and fine stitching allow it to catch even the smallest food waste.
·Shopping bag
These bags contain some biomass. They are as strong as PE bags and help reduce CO2 emissions.